Automated Cleft Speech EvaluationCleft lip and/or palate is the most common craniofacial birth anomaly, affecting 1 in 700 children born in the USA, and 200,000 worldwide each year. Even after the palate has been repaired, many children will need further care to speak normally but evaluation of cleft speech remains subject to bias with variations across the country, and there is a severe shortage of cleft speech pathologists globally.
I am developing a fully automated cleft speech evaluator using a computer learning system. It uses a specially adapted speech recognition engine to distinguish between normal speech and the speech problems found in children with cleft palate. In particular, it distinguishes between speech problems that need to be corrected with surgery, and speech problems that can be helped with speech therapy. While it is still in the very early stages of development without enough training data to expect it function well yet, already the evaluator concurs with experienced craniofacial speech pathologists on 85% of evaluations. |
Automated Cleft Speech Evaluation Using Speech Recognition
Vucovich M, Hallac RR, Kane AA, Cook J, Van’T Slot C, Seaward JR J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017 May 5 [Epub ahead of print] doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2017.05.002 |
|
Dynamic Facial Asymmetry in Patients with Repaired Cleft Lip using 4D Imaging (Video Stereophotogrammetry)
Hallac RR, Feng J, Kane AA, Seaward JR J Cranmaxfac Surg 2017; 45(1):8-12: 10.1016/j.jcms.2016.11.005 |
Dynamic Facial ExpressionsChildren born with a unilateral cleft lip have asymmetry of the muscles of the upper lip as well as the asymmetry from the cleft scar. Cleft lip repair attempts to minimize this asymmetry, but some difference between the two sides inevitably persists.
There are plenty Studies investigating asymmetry in patients with cleft lip have used facial measurements, and static 2D and 3D photography. The nose/lip/mouth area, however, is rarely static in our day to day social interactions. By using 4D imaging (video 3D stereophotogrammetry) we can investigate not only the asymmetry in facial expressions but the asymmetry in the way the muscles of the face move to make these expressions. This can help with improving outcomes from cleft lip surgery. |
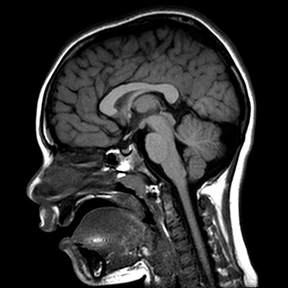
Speech Evaluation without X-rays - Real-time MRI scanning for speechChildren born with a cleft palate can struggle to produce normal sounding speech, either because their palate isn't moving well enough to be an effective valve to block air escaping out of the nose or because of the way they have learnt to make certain sounds.
Prior to planning surgery for cleft speech, we will typically investigate the palate movement using an x-ray video and / or a camera inserted into the nose. As the x-ray study involves radiation, and the camera study is uncomfortable, I would like to find a safe and pleasant alternative to these imaging studies. By using a type of MRI scanning, we can look at how the soft palate moves without any radiation exposure or invasive cameras for the child. |
|
Automated Cleft Speech Evaluation Using Speech Recognition
Vucovich M, Hallac RR, Kane AA, Cook J, Van’T Slot C, Seaward JR J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017 May 5 [Epub ahead of print] doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2017.05.002 |
Perception of facial differences - eye trackingAs humans, we are very good at looking at a face or head, and making a snap decision about whether that face looks normal or abnormal; and as a cleft and craniofacial surgeon, I strive to give my patients outcomes that will result in them falling into the 'normal' group.
It isn't clear how we make that snap decision and what components of head shape, facial shape, symmetry and features we use to make this evaluation of others' faces. I am using eye-tracking technology to help shed some light on how we evaluate a face and head during interactions, and what features are most important when we decide what makes a face 'normal'. |
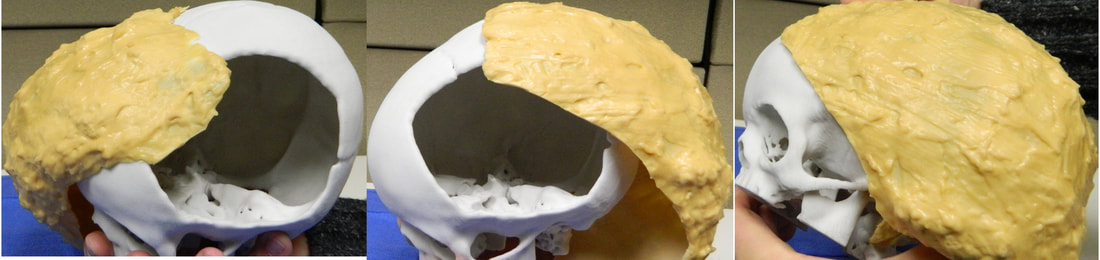
Customizing surgical planning - 3D printing and moldable materials3D printing is an expanding field within surgery, but most 3D printers for surgical applications print 'hard' materials, like plaster and plastic. This is fine for modelling hard tissues, such as bone, but is inadequate for surgical planning for skin and soft tissue reconstruction planning.
I have developed techniques using latex and silicone to model soft tissues over 3D printed bony structures, to help with complex surgical planning. |
Liquid Latex Molding: A Novel Application of 3D Printing to Facilitate Flap Design
Cho MJ, Kane AA, Hallac RR, Gangopadhyay N, Seaward JR Cleft Palate Craniofacial J 2016; May 2 [Epub ahead of print] doi: 10.1597/15-252 |
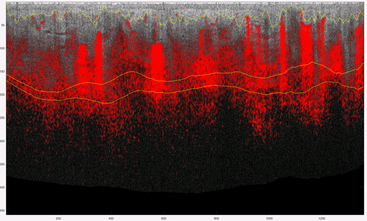
Improving Laser treatment outcomes - visualizing the vasculature of the individual childWhen we use vascular lasers for capillary malformation, there is often excellent fading of the red area with the first few treatments, but once it has faded to a light pink, the improvement is less predictable. This is likely because the blood vessels in the capillary malformation are out of reach of the laser light, which only travels about 1mm into the skin. We are looking at where the blood vessels are in the skin, and how the position changes with laser treatments. By using a technology called Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), we can examine the blood flow in various levels of the skin and hope to use this information to help choose the type of laser, and the ideal laser settings to give the best outcome from each treatment.
|
Publications
Textbook Chapters
Distraction Osteogenesis
Seaward JR & Kane AA. Mitchell R (Section Editor) Kountakis S (editor)
Encyclopedia of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery
Springer-Verlag. 2013 ISBN 978-3-642-23498-9
The Evidence for Prophylaxis to Prevent Venothromboembolic Disease in Plastic Surgery Patients
Seaward JR & Watts AM. Stone C (editor)
The Evidence for Plastic Surgery
TFM Publishing Ltd. 2008. ISBN 978-1-903-37850-2
Cracking the MRCS Viva
Au-Yong I, Howarth S, Tang T, Sayers R
Hodder Arnold 2006. ISBN 978-0-340-90646-0
Plastic Surgery and Burns Specialist Contributor
Invited Articles
Ferraro’s Fundamentals of Maxillofacial Surgery, 2nd Edition
Seaward JR, Kane AA.
Plast Recon Surg 2015; 136(6):1389-90 doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000001824.
Syndromic Craniosynostosis
Seaward JR & Derderian C
Semin Plast Surg 2012; 26(2): 64-75 doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1320064
Original Articles
Automated Cleft Speech Evaluation Using Speech Recognition
Vucovich M, Hallac RR, Kane AA, Cook J, Van’T Slot C, Seaward JR
J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017 May 5 [Epub ahead of print] doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2017.05.002
Three-dimensional changes in head shape after extended sagittal strip craniectomy with wedge ostectomies and helmet therapy
Chou PY, Hallac RR, Patel S, Cho MJ, Stewart N, Smartt JM, Seaward JR, Kane AA, Derderian CA.
J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2017; 19(6):684-689 doi: 10.3171/2017.1.PEDS16660
Dynamic Facial Asymmetry in Patients with Repaired Cleft Lip using 4D Imaging (Video Stereophotogrammetry)
Hallac RR, Feng J, Kane AA, Seaward JR
J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2017; 45(1):8-12 doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2016.11.005
Impact of Long Flexor Versus Intrinsic Dominance in the Generation of Arc of Finger Flexion
Seaward JR, Peck F, Lees VC
Hand 2016; 11(3): 364-367 doi: 10.1177/1558944715620796
Metopic “ridge” vs craniosynostosis”; Quantifying severity with 3D curvature analysis
Cho MJ, Kane AA, Seaward JR, Hallac RR
J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2016; 44(9):1259-65 doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2016.06.019
Ionizing Radiation in Craniofacial Surgery: a Primer on Dose and Risks
Cho MJ, Blackburn T, Hallac R, Kane AA, Koral K, Seaward JR
Cleft Palate Craniofacial J 2016; May 2 [Epub ahead of print] doi: 10.1597/15-350
Liquid Latex Molding: A Novel Application of 3D Printing to Facilitate Flap Design
Cho MJ, Kane AA, Hallac RR, Gangopadhyay N, Seaward JR
Cleft Palate Craniofacial J 2016; May 2 [Epub ahead of print] doi: 10.1597/15-252
Objective and Subjective Image Evaluation of Maxillary Alveolar Bone Based on Cone-Beam CT Exposure Parameters
de Moura PM, Hallac RR, Seaward JR, Kane AA, Aguiar M, Raggio R, Gutfilen B
Oral Surg, Oral Med, Oral Path, Oral Rad 2016; 121(5):557-65 doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2016.01.019
Should We Give Routine Postoperative Intravenous Fluids After Cleft Surgery?
Onyekwelu O, Seaward J, Beale, V
Cleft Palate Craniofacial J 2016; 53(2): e18-e22 doi: 10.1597/14-078.1
Improving the Evaluation of Alveolar Bone Grafts With Cone Beam Computerized Tomography
de Moura PM, Hallac R, Kane A, Seaward J
Cleft Palate Craniofacial J 2016 Jan;53(1):57-63 doi: 10.1597/14-304
The Effects of Whole-Vault Cranioplasty versus Strip Craniectomy on Long-Term Neuropsychological Outcomes in Sagittal Craniosynostosis
Derderian CA, Heppner C, Cradock MM, Woo AS, Patel KB, Smyth MD, Viera P, Weprin BE, Seaward J, Smartt JM, Kane AA
Plast Recon Surg 2015; 136(1): 114e-115e. doi: 10.1097/PRS. 000000000001344
Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis
Seaward JR & Kane AA
Newsletter of the Pediatric Society of Greater Dallas. Spring 2012 p. 2
Computer Aided Surgical Planning in the Treatment of Soft Tissue Sarcoma
Seaward JR, Wilson PA, Stone CA
Ann R Coll Surg 2010; 92(8): 639-642 doi: 10.1308/003588410X12699663904556
Supraorbital neuroma masquerading as local recurrence from a previously excised microcystic adnexal carcinoma
Seaward JR, Kalipershad SNR, Ross GL
J Plast, Recon Aest Surg 2010; 63(3): e239-41 doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2009.07.013
Providing a Plastic Surgery Service in the New NHS
Seaward JR, Bryant M, Oliver DW
Bulletin of the Royal College of Surgeons of England 2007 Vol. 89 No. 9 pp. 322-326
A Functional Neuroanatomy of Hallucinations in Schizophrenia
Silbersweig DA, Stern E, Frith C, Cahill C, Holmes A, Grootoonk S, Seaward J, McKenna P, Chua SE, Schnorr L, Jones T, Frackowiak RSJ
Nature 1995; 378(6553): 176-179 doi: 10.1038/378176a0
The Development of In-Vivo Tracer Methods to Obtain New Information about Human Disease - A Study of the Hallucinating Brain
Jones T, Silbersweig DA, Stern E, Schnorr L, Seaward J, Clark JC, Lammertsma AA, Grootoonk S
Eur J Nucl Med 1996; 23(3): 332-335
Deficits in Cerebral Glucose-Metabolism Demonstrated by Positron Emission Tomography in Individuals At Risk of Familial Alzheimer’s-Disease
Kennedy AM, Frackowiak RSJ, Newman SK, Bloomfield PM, Seaward J, Roques P, Lewington G, Cunningham VJ, Rossor MN
Neurosci Lett 1995; 186(1): 17-20
Distraction Osteogenesis
Seaward JR & Kane AA. Mitchell R (Section Editor) Kountakis S (editor)
Encyclopedia of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery
Springer-Verlag. 2013 ISBN 978-3-642-23498-9
The Evidence for Prophylaxis to Prevent Venothromboembolic Disease in Plastic Surgery Patients
Seaward JR & Watts AM. Stone C (editor)
The Evidence for Plastic Surgery
TFM Publishing Ltd. 2008. ISBN 978-1-903-37850-2
Cracking the MRCS Viva
Au-Yong I, Howarth S, Tang T, Sayers R
Hodder Arnold 2006. ISBN 978-0-340-90646-0
Plastic Surgery and Burns Specialist Contributor
Invited Articles
Ferraro’s Fundamentals of Maxillofacial Surgery, 2nd Edition
Seaward JR, Kane AA.
Plast Recon Surg 2015; 136(6):1389-90 doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000001824.
Syndromic Craniosynostosis
Seaward JR & Derderian C
Semin Plast Surg 2012; 26(2): 64-75 doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1320064
Original Articles
Automated Cleft Speech Evaluation Using Speech Recognition
Vucovich M, Hallac RR, Kane AA, Cook J, Van’T Slot C, Seaward JR
J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017 May 5 [Epub ahead of print] doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2017.05.002
Three-dimensional changes in head shape after extended sagittal strip craniectomy with wedge ostectomies and helmet therapy
Chou PY, Hallac RR, Patel S, Cho MJ, Stewart N, Smartt JM, Seaward JR, Kane AA, Derderian CA.
J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2017; 19(6):684-689 doi: 10.3171/2017.1.PEDS16660
Dynamic Facial Asymmetry in Patients with Repaired Cleft Lip using 4D Imaging (Video Stereophotogrammetry)
Hallac RR, Feng J, Kane AA, Seaward JR
J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2017; 45(1):8-12 doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2016.11.005
Impact of Long Flexor Versus Intrinsic Dominance in the Generation of Arc of Finger Flexion
Seaward JR, Peck F, Lees VC
Hand 2016; 11(3): 364-367 doi: 10.1177/1558944715620796
Metopic “ridge” vs craniosynostosis”; Quantifying severity with 3D curvature analysis
Cho MJ, Kane AA, Seaward JR, Hallac RR
J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2016; 44(9):1259-65 doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2016.06.019
Ionizing Radiation in Craniofacial Surgery: a Primer on Dose and Risks
Cho MJ, Blackburn T, Hallac R, Kane AA, Koral K, Seaward JR
Cleft Palate Craniofacial J 2016; May 2 [Epub ahead of print] doi: 10.1597/15-350
Liquid Latex Molding: A Novel Application of 3D Printing to Facilitate Flap Design
Cho MJ, Kane AA, Hallac RR, Gangopadhyay N, Seaward JR
Cleft Palate Craniofacial J 2016; May 2 [Epub ahead of print] doi: 10.1597/15-252
Objective and Subjective Image Evaluation of Maxillary Alveolar Bone Based on Cone-Beam CT Exposure Parameters
de Moura PM, Hallac RR, Seaward JR, Kane AA, Aguiar M, Raggio R, Gutfilen B
Oral Surg, Oral Med, Oral Path, Oral Rad 2016; 121(5):557-65 doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2016.01.019
Should We Give Routine Postoperative Intravenous Fluids After Cleft Surgery?
Onyekwelu O, Seaward J, Beale, V
Cleft Palate Craniofacial J 2016; 53(2): e18-e22 doi: 10.1597/14-078.1
Improving the Evaluation of Alveolar Bone Grafts With Cone Beam Computerized Tomography
de Moura PM, Hallac R, Kane A, Seaward J
Cleft Palate Craniofacial J 2016 Jan;53(1):57-63 doi: 10.1597/14-304
The Effects of Whole-Vault Cranioplasty versus Strip Craniectomy on Long-Term Neuropsychological Outcomes in Sagittal Craniosynostosis
Derderian CA, Heppner C, Cradock MM, Woo AS, Patel KB, Smyth MD, Viera P, Weprin BE, Seaward J, Smartt JM, Kane AA
Plast Recon Surg 2015; 136(1): 114e-115e. doi: 10.1097/PRS. 000000000001344
Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis
Seaward JR & Kane AA
Newsletter of the Pediatric Society of Greater Dallas. Spring 2012 p. 2
Computer Aided Surgical Planning in the Treatment of Soft Tissue Sarcoma
Seaward JR, Wilson PA, Stone CA
Ann R Coll Surg 2010; 92(8): 639-642 doi: 10.1308/003588410X12699663904556
Supraorbital neuroma masquerading as local recurrence from a previously excised microcystic adnexal carcinoma
Seaward JR, Kalipershad SNR, Ross GL
J Plast, Recon Aest Surg 2010; 63(3): e239-41 doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2009.07.013
Providing a Plastic Surgery Service in the New NHS
Seaward JR, Bryant M, Oliver DW
Bulletin of the Royal College of Surgeons of England 2007 Vol. 89 No. 9 pp. 322-326
A Functional Neuroanatomy of Hallucinations in Schizophrenia
Silbersweig DA, Stern E, Frith C, Cahill C, Holmes A, Grootoonk S, Seaward J, McKenna P, Chua SE, Schnorr L, Jones T, Frackowiak RSJ
Nature 1995; 378(6553): 176-179 doi: 10.1038/378176a0
The Development of In-Vivo Tracer Methods to Obtain New Information about Human Disease - A Study of the Hallucinating Brain
Jones T, Silbersweig DA, Stern E, Schnorr L, Seaward J, Clark JC, Lammertsma AA, Grootoonk S
Eur J Nucl Med 1996; 23(3): 332-335
Deficits in Cerebral Glucose-Metabolism Demonstrated by Positron Emission Tomography in Individuals At Risk of Familial Alzheimer’s-Disease
Kennedy AM, Frackowiak RSJ, Newman SK, Bloomfield PM, Seaward J, Roques P, Lewington G, Cunningham VJ, Rossor MN
Neurosci Lett 1995; 186(1): 17-20